Is the Mean Always Greater Than the Median
Again the mean reflects the skewing the most. When a data set has a symmetrical distribution the mean and the median are close together because the middle value in the data set when ordered smallest to largest resembles the balancing point in the data which occurs at the average.
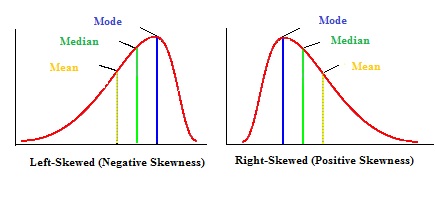
Skewed Distribution Definition Examples Statistics How To
The mean will be lower than the median in any distribution where the values fall off or decrease from the middle value faster than they increase from the middle value.

. To summarize generally if the distribution of data is skewed to the left the mean is less than the median which is often less than the mode. The mean will have a higher value than the median. Different types of measures of central tendency are- 1 Mean.
Answer 1 of 13. For a data set half of the observations are always greater. If the distribution of data is skewed to the right the mode is often less.
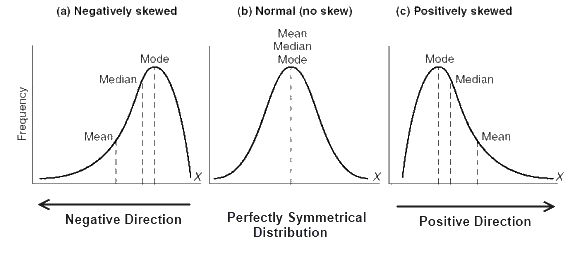
In case of a positively skewed frequency distribution the mean is always greater than median and the median is always greater than the mode. 100 1 rating Measures of central tendency are the numbers that summarise the data. In which case the skewness is greater than zero.
View the full answer. The median is better suited for skewed distributions to derive at central tendency. This is much less common than the reverse.
In a normal distribution the median is always greater than the mean. What does the difference between mean and median suggest. When a data set has a symmetrical distribution the mean and the median are close together because the middle value in the data set when ordered smallest to largest resembles the balancing point in the data which occurs at the average.
Another characteristic is that when there are negatively skewed distributions the. They describe what is the average or typical value of the distribution. Choose the correct answer below.
If the distribution of data is skewed to the right the mode is often less than the median which is less than the mean. In such a distribution usually but not always the mean is greater than the median or equivalently the mean is greater than the mode. In a normal distribution the mean is always greater than the median.
Usually its because the distribution is left-skewed. It is the mathematical equivalent to the median. Mean Median Mode For Positively Skewed Frequency Distribution In case of a positively skewed frequency distribution the mean is always greater than median and the median is always greater than the mode.
Is the mean always lower than the median. In a normal distribution the mean is always greater than the median. The median of a set of numbers is the value that is in the middle In a set with an odd number of values its the middle value.
To summarize generally if the distribution of data is skewed to the left the mean is less than the median which is often less than the mode. In such a distribution usually but not always the mean is greater than the median or equivalently the mean is greater than the mode. For any evenly spaced set the mean of the set is always equal to the median.
Is the mean always greater than the median in a right skewed distribution. In a normal distribution the mean and median are equal. In a negatively skewed distribution the mean is usually less than the median because the few low scores tend to shift the mean to the left.
Many will be close to the maximum but there will be. It is always greater than the arithmetic mean. Why mean and median are not the same.
Is The Mean Always More Accurate Than The Median. Is the mean equal to the median. Answer 1 of 7.
Just add up all the numbers then divide by the number of numbers. When that is the case the median is a greater measure of. That is it has a long tail to the lower end.
The distribution is said to be right-skewed. In a positively skewed distribution the mean is usually greater than the median because the few high scores tend to shift the mean to the right. Combining them gives an indication of dispersion much the same as standard.
For example for a bell-shaped. You just studied 2 terms. As a general rule when data is skewed to the right positively skewed the mean will be greater than the median and when data is skewed to the left negatively skewed the median will typically be greater than the mean.
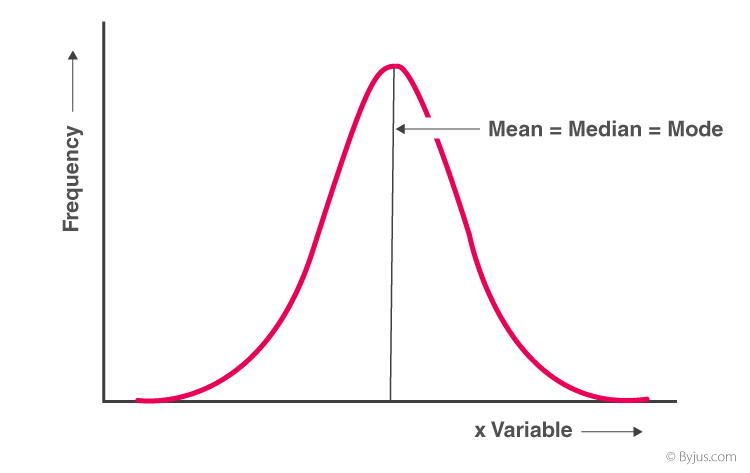
If a frequency distribution graph has a symmetrical frequency curve then mean median and mode will be equal. Both the median and mean and the mode are measures of central tendency but the median balances observations whereas the mean balances values. Mean is the arithmetic average of the values.
In a perfectly symmetrical distribution the mean and the median are the same. Both it is the mathematical equivalent to the median and it is always less than or equal to the arithmetic mean. What does it mean if data is skewed right.
Is the median always greater than the mean. One of the basic tenets of statistics that every student learns in about the second week of intro stats is that in a skewed distribution the mean is closer to the tail in a skewed distribution. Median is preferable significantly when you may have some excessive high and low values within the knowledge distribution.
One of the characteristics of mean when measuring central tendency is that when there are positively skewed distributions the mean is always greater than the median. Which of the following is usually true when a distribution of data is skewed right. So in a right skewed distribution the tail points right on the number line the mean is higher than the median.
A skewed right distribution is one in which the tail is on the right side. The Difference Between Mean and Median The mean is the average you already know. The mean is not a robust tool since it is largely influenced by outliers.
The mean will have a higher value than the median. One example would be the SATs of students in Ivy League schools. In which case the skewness is greater than zero.
Is the median always lower than the mean. You just studied 2 terms. In a normal distribution the mean and median are equal.
As a general rule when data is skewed to the right positively skewed the mean will be greater than the median and when data is skewed to the left negatively skewed the median will typically be greater than the mean.

Mean And Standard Deviation Or Median And Quartiles Tidsskrift For Den Norske Legeforening

Mean And Standard Deviation Or Median And Quartiles Tidsskrift For Den Norske Legeforening

Understanding Measures Of Central Tendency Magoosh Statistics Blog

Understanding Measures Of Central Tendency Magoosh Statistics Blog
Relation Between Mean Median And Mode With Solved Example Questions

Math Pennants Are A Fun Way To Show Off Student Work Math Pennant Middle School Math Classroom Decorations Math Classroom Decorations

Relation Between Mean Median And Mode With Solved Example Questions

Amh Levels By Age Graphing Unanswered Prayers Medical
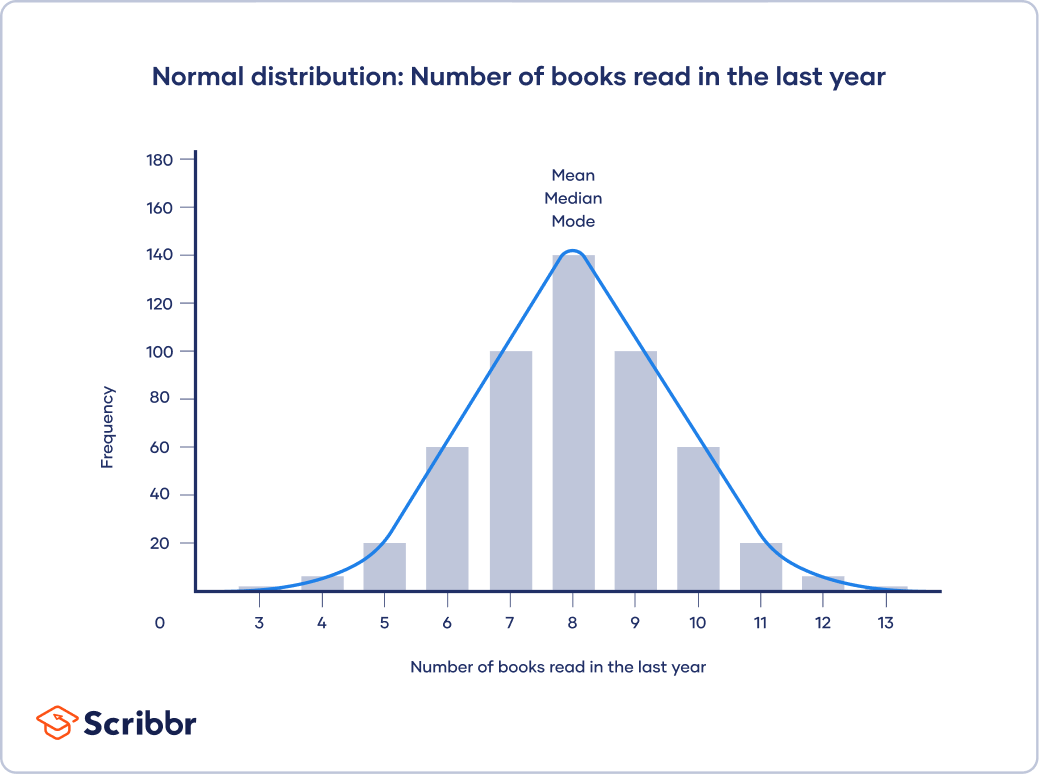
Central Tendency Understanding The Mean Median And Mode

Pin By Jolee Withers On Wrd Week 3 Relatable Scores Personalized Items

Difference Between Mean And Median With Conmparison Chart Key Differences
Data Science Statistics Interview Questions Answers

Mean Median And Standard Deviation Concepts Working With Data Using Evidence For Learning Home Assessment
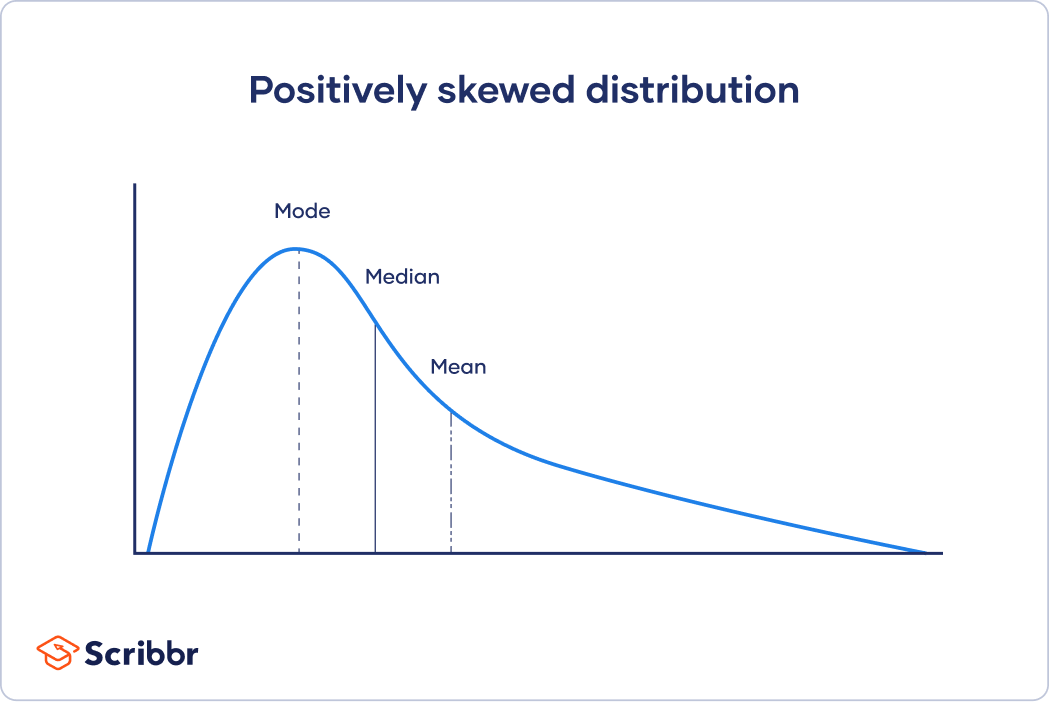
The Median What Is It And How Do You Find It
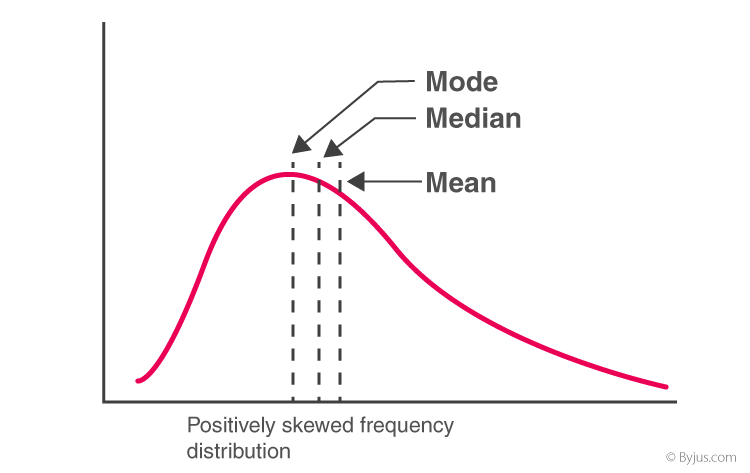
Relation Between Mean Median And Mode With Solved Example Questions
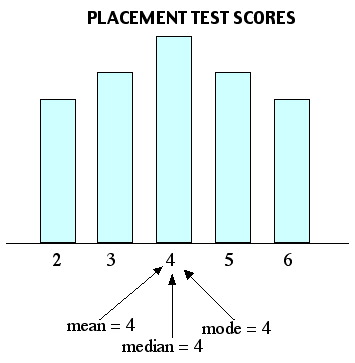
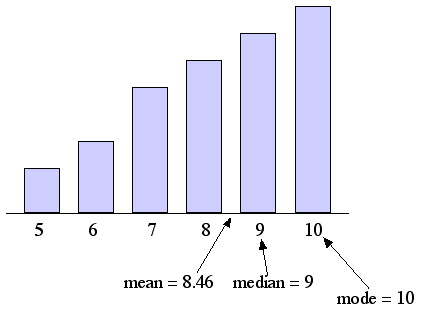
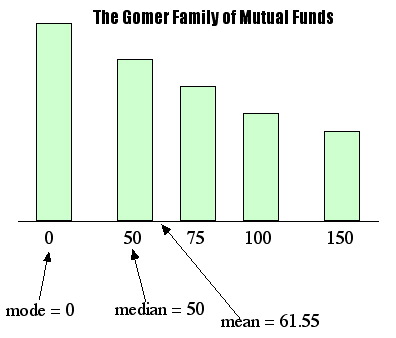
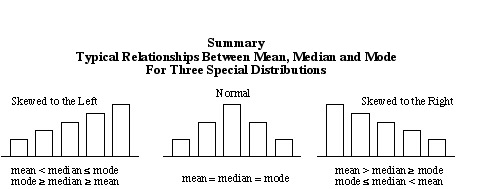
Comments
Post a Comment